TCP/ IP Model: Layer, Protocol & Function –
What is TCP/ IP Reference Model?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP) are two separate computer network protocol that define a set of rules which is helps all the connected devices are communicated with each other in a network.
Characteristics: –
i) TCP/ IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol.
ii) It was developed by Department of Defense in 1970.
iii) It is a suite of communication protocol.
iv) It was developed prior to the OSI model.
v) It is not to the same as the OSI model.
vi) It is also called as Internet Model or DoD Model or DARPA Model.
vii) TCP/ IP model maintained by the IETF.
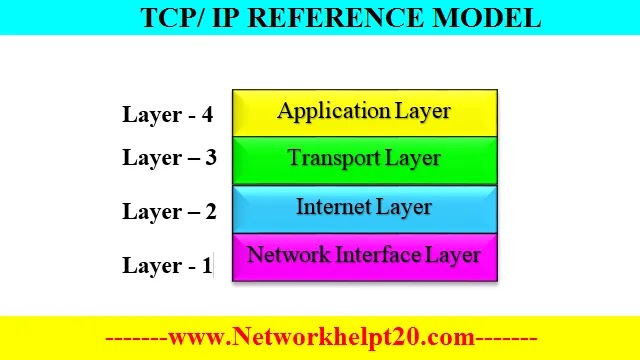
viii) The TCP/ IP model consists of 4 layers –
1) Network Interface Layer
2) Internet Layer
3) Transport Layer
4) Application Layer
Function of TCP/ IP Model: –
1) Network Interface Layer: –
Characteristics: –
i) The Network Interface layer is the lowest layer of the TCP/ IP model.
ii) It is combination function of the Physical Layer and Data Link Layer as well as OSI Model.
iii) It is defined of how data is physically sent through the network.
iv) It is responsible for transmission of the data between the connected devices in a network.
v) Here uses network medium are the Co-axial Cable, Optic Fiber Cable, Twisted-pair Cable.
vi) Here uses network protocol are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc.
2) Internet Layer: –
Characteristics: –
i) An Internet Layer is a second layer of TCP/ IP model.
ii) It is responsible for accepting, routing and delivering the data packets.
iii) This layer is same as well as Network Layer of the OSI model.
iv) Here uses protocol are IP, ARP, ICMP, IGMP.
v) It is also known as Network Layer.
3) Transport Layer: –
Characteristics: –
i) Transport Layer is the third layer of TCP/ IP model.
ii) Transport Layer is responsible for end-to-end communication and error free data delivery.
iii) The Transport Layer is responsible for Flow Control, Error Control and Segmentation or De-segmentation of the data.
iv) It is also responsible for acknowledgement of the successfully data transmission and re-transmitting the data.
v) The Transport Layer adds header to the data.
vi) Here uses protocol are TCP and UDP.
vii) It is also called as Host-to-Host layer.
4) Application Layer: –
Characteristics: –
i) Application Layer is the topmost layer of the TCP/ IP model.
ii) Its function same as well as Application, Presentation and Session Layer of the OSI model.
iii) Here users are interacted with the applications.
iv) It is responsible for high-level protocols.
v) It is provided e-mail services.
vi) Here use protocols are HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, RIP, TELNET, SSH etc.
[Note: – NITA – N for Network Interface Layer, I for Internet Layer, T foe Transport Layer, A for Application Layer]
Importance Protocols of TCP/ IP Model
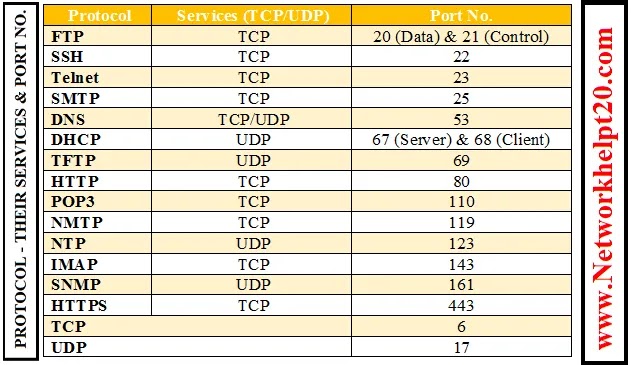
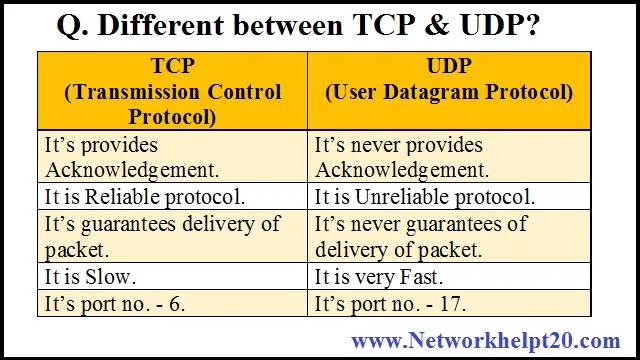
1. TCP: –
i) It stands for Transmission Control Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 6.
iii) It is a connection-oriented protocol.
iv) It provides Acknowledgement while data is transmitting.
v) It is a reliable protocol.
vi) Its guarantees of delivery of packets.
vii) It is very slow.
2. UDP: –
i) It stands for User Datagram Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 17.
iii) It is a connection less protocol.
iv) Its never provides Acknowledgement while data is transmitting.
v) It is very fast.
vi) It is an unreliable protocol.
vii) It’s never guarantees delivery of packets.
3. TELNET: –
i) It stands for Teletype Network.
ii) It is a terminal emulation protocol of TCP/ IP model.
iii) It is an Application Layer protocol.
iv) It is uses port no. 23.
v) It is a secure service because it needs administrator login and password.
vi) You can configure remote device such as Router, Switches.
4. SSH: –
i) Its stands for Secure Shell.
ii) Its port no. 22.
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It provides remote login and secure file access.
5. FTP: –
i) It stands for File Transfer Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 20 for Data and 21 for Control.
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for File Upload and Download services.
v) It is responsible for process to process data delivery.
6. TFTP: –
i) It stands for Trivial File Transfer Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 69.
iii) It is an Application Layer protocol.
iv) It is a TCP base service protocol.
v) It is used for Web Services.
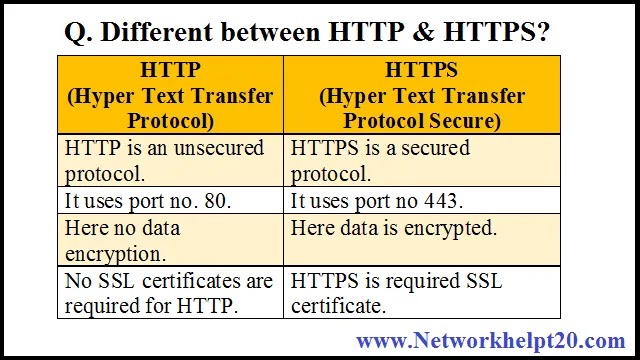
7. HTTP: –
i) It stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 80.
iii) It is an Application Layer protocol.
iv) It is a TCP base service protocol.
v) It is used for Web Service.
8. HTTPS: –
i) It stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure.
ii) Its port no. 443.
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for Web Service in Secure way.
9. SMTP: –
i) It stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 25.
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for Sending Mail.
10. POP3: –
i) Its stand for Post Office Protocol version 3.
ii) Its port no. 110.
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for Receiving Mail.
11. IMAP: –
i) Its stands for Internet Mailing Application Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 143
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for Receiving Mail.
12. DNS: –
i) It stands for Domain Name Service.
ii) Its port no. 53.
iii) It is a TCP/ UDP both service protocol.
iv) It is used for name resolution service.
13. DHCP: –
i) Its stand for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
ii) Its port no 67 for Server and 68 for Client.
iii) It is a UDP base service protocol.
iv) It helps automatically assign an IP address to a computer.
14. NNTP: –
i) It stands for Network News Transmission Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 119.
iii) It is a TCP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for news group service.
15. SNMP: –
i) Its stand for Secure Network Management Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 161.
iii) It is an UDP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for network management.
16. NTP: –
i) Its stand for Network Time Protocol.
ii) Its port no. 123.
iii) It is an UDP base service protocol.
iv) It is used for clock synchronization between computer system and packet switched.
Protocol Name – their Services & Port No.
TCP/ IP INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
Q. What is TCP/IP Model?
Ans: – Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol are two separate protocol which define a set of rules which is help in communicated to connected devices in a network. It was developed by DoD (department of Defense) in 1970.
Q. Who are maintained of TCP/ IP Model?
Ans: – IETF.
Q. What is IETF?
Ans: – It stands for Internet Engineering Task Force. It is an open standard organization which is develop, designer, operators, vendors and researchers concerned.
Q. What is DARPA?
Ans: – It stands for Defense Advanced Research Project Agency. It is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Q. What are the layers of TCP/ IP Model?
Ans: – TCP/ IP models consist of 4 layers –
1. Network Interface Layer
2. Internet Layer
3. Transport Layer
4. Application Layer
Q. Different between TCP & UDP?
Ans: –
Q. What is Protocol?
Ans: – A Protocol is a special set of rules which followed by the computer to communicated with each other on a network.
Q. What is RFC?
Ans: – RFC stands for Request for Comments. It is a standard publication of IETF where standard and technical development of protocol are defined.
Q. What is ARP?
Ans: – Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is resolved MAC address to a known IP address.
Q. What is RARP?
Ans: – Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is resolved MAC address to a known IP address.
Q. What is TCP?
Ans: – Transmission Control Protocol is a reliable Transport Layer protocol which is used for re-transmission, sequencing and fragmentation of the data.
Q. What is UDP?
Ans: – User Datagram Protocol is a fast but unreliable protocol which is used for small data packets transfer.
Q. What is RIP?
Ans: – Routing Information Protocol is a distance vector protocol in network.
Q. What is SLIP?
Ans: – Serial Line Internet Protocol is the protocol for the carrying IP information over serial links.
Q. What is ICMP?
Ans: – It stands for Internet Control Message Protocol. It is defining by IETF RFC 792. It is a Network Layer protocol of the TCP/ IP suite used by hosts and gateways to sent notification of datagram problem back to the sender.
Q. What is different between HTTP & HTTPS?
Ans: –
Q. What is different between POP3 & IMAP?
Ans: –
Also Read: –
• Top 160 Networking Interview Questions & Answers
• Top 115 CCNA Interview Questions & Answers
• Top 60 Linux System Administrator Interview Questions
• Top 50 Linux Interview Questions & Answers
• Computer basic Troubleshooting Interview Questions with Answers
• Computer Hardware MCQ Questions & Answers
• Computer Network MCQ Questions & Answers
• Network-Devices-Hub-Repeater-Bridge-Switch-Router-Gateways
• Computer-network-transmission-mode
• Describe straight-through and cross-over cable
• What is Transmission Media & Types of Transmission Media
• Types of Computer Network
• What is Operating System
• Network Topology
• Describr OSI model
• Processor (CPU) in Computer
• What is BIOS
• What is Hard Disk
• RAM (Random Access Memory) definition
• CMOS Definition
• Basic parts of a Computer
• Motherboard Definition Types Components Ports
• Components of switched mode power supply
• Components of computer system
• Computer Input Output Devices
• Different between Intel i-series processor Generation
• Microsoft Windows History
—o—